Lepcis Magna
Type:
Cities
Date:
Founded in the seventh century BCE, with important expansions and new building projects beginning in the late second century
Location or Findspot (Modern-Day Country):
Libya
Description:
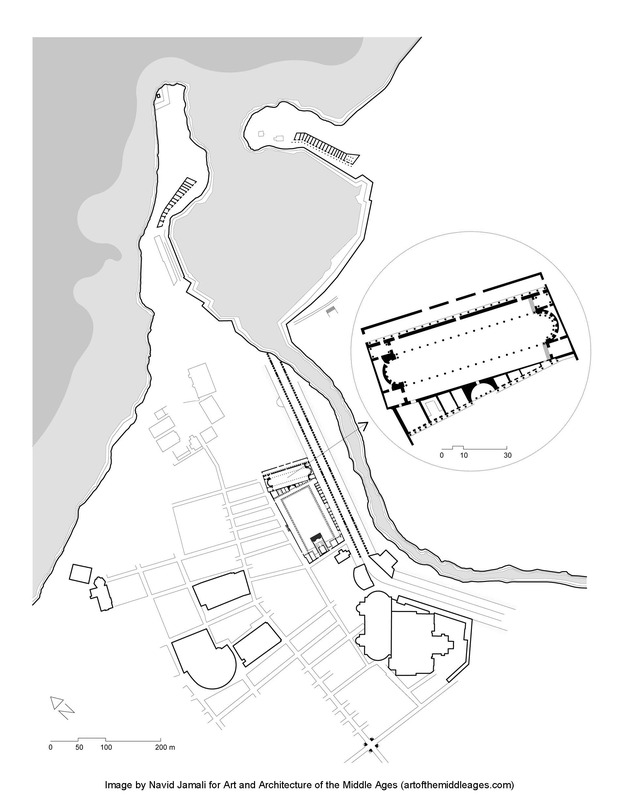
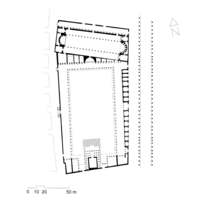
The Roman Emperor Septimius Severus (r. 197–211 CE) was a native of Lepcis Magna, a city he enriched with a new forum, a four-way arch, a wide colonnaded street, a basilica, and other lavish buildings. The ruins of this important Roman city were excavated starting in 1920 and are among the best preserved Mediterranean sites from the period. The remains of the colonnaded street feature heads of gorgons, mythical creatures from Greek mythology with snaky hair (like the well-known Medusa).
The Latin inscription on both the interior and exterior of the basilica reads:
The Latin inscription on both the interior and exterior of the basilica reads:
"The emperor Caesar Lucius Septimius [Severus Pius] Pert [inax Augustus, victor in Arabia, victor in Adiabene, greatest victor in Parthia, greatest victor in Britannia, ] chief priest, [holding tribunician] power for the eighteenth time, acclaimed victor twelve times, consul [three times, father] of the country, proconsul, began and substantially completed (this); emperor Caesar, son of deified Septimius Severus Pius, victor in Arabia, victor in Adiabene, greatest victor in Parthia, greatest victor in Britannia, grandson of deified Marcus Antoninus, victor in Germany, victor in Sarmatia, great grandson of deified Antoninus Pius, great great grandson of deified Hadrian, great great great grandson of deified Trajan, victor in Parthia and of deified Nerva, emperor Caesar Marcus Aurellius Antoninus Pius Augustus, greatest victor in Parthia, greatest victor in Britannia, greatest victor in Germany, chief priest, holding tribunician power for the nineteenth time, acclaimed victor three times, consul four times, father of the country, proconsul, [arranged] for its completion."—from Inscriptions of Roman Tripolitania, http://inslib.kcl.ac.uk/irt2009/IRT428.html
Relevant Textbook Chapter(s):
1
Repository and Online Resources:
• Visit the UNESCO page on Lepcis Magna.
• Watch a video on the archeological site.
• Explore an interactive 3D model of Lepcis Magna.
Image Credits:
Joe and Clair Carnegie; Navid Jamali